CacheGuard-OS
CacheGuard-OSUser's Guide - Version UF-2.5.1
General Modes
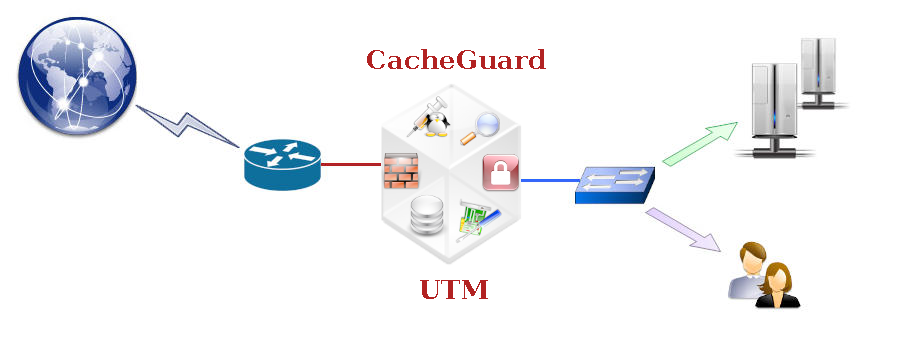
A CacheGuard appliance is an integrated system that secures and optimises Internet traffic by providing a comprehensive range of features. To achieve an optimised configuration, it is recommended that you activate only the features you actually need and deactivate all others. However, if required, it is possible to activate all available features simultaneously on the same appliance, and all activated features will operate seamlessly and efficiently together.The mode command allows you to activate or deactivate different features known as modes. For almost all modes, there is a command with the same name that allows you to configure that mode. For example, the embedded firewall can be activated using the mode firewall on command, and the firewall can be configured using the firewall command. There are two main groups of modes: network modes and function modes. The sections below provide a brief description of all available modes. Note that the apply command must be invoked after activating or deactivating a mode.
Network Modes
This section provides a brief description of all network modes. Available network modes operate at the TCP/UDP IP layer and are as follows:- DHCP Server
- Caching DNS
- High Availability
- Passive FTP
- Quality of Service
- Network Router
- Source NAT
- Transparent Web
- Transparent Web SNAT
- Tagged VLANs
DHCP Server
A CacheGuard appliance integrates a DHCP server to dynamically assign IP addresses to connected devices. To activate the DHCP server, use the mode dhcp on command. You can configure the DHCP server using the dhcp command. This command allows you to define dynamic IP ranges and, if necessary, reserve IP addresses for specific devices.Caching DNS
A CacheGuard appliance integrates a caching-only Domain Name Server that can be used by all other integrated services as well as by external clients. To activate the integrated DNS server and make it available for external use, execute the following commands:- dns raz
- dns add localhost
- mode dns on
High Availability
Two or more CacheGuard appliances can be deployed in HA (High Availability) mode using the VRRP protocol. In addition, network interfaces (external, internal, etc.) of a CacheGuard appliance can be associated with multiple physical interfaces to provide link redundancy. To activate HA mode, use the mode ha on command. Once HA mode is activated, use the vrrp command to associate one or more VRRP IP addresses with at least one network interface. To associate more than one physical network interface with a logical interface, use the link command.Passive FTP
By default, a CacheGuard appliance uses the passive FTP protocol to initiate FTP sessions with external FTP servers. To use active FTP mode instead, you must deactivate passive FTP mode by using the mode ftppassive off command. Please note that switching between passive and active FTP modes is done globally (it cannot be set per FTP session).Quality of Service
A CacheGuard appliance can shape and schedule network traffic to offer QoS (Quality of Service) to users and applications. Using the QoS manager in a CacheGuard appliance allows you to reserve network bandwidth for critical applications. To activate QoS mode, use the mode qos on command. You can then configure traffic shaping using the qos command. All traffic destined for services (proxy, antivirus, etc.) running on the appliance itself, as well as routed traffic passing through it, is managed by the QoS system.Network Router
A CacheGuard appliance can act as a network router supporting static routes and multi-gateway configurations. Use the mode router on command to activate router mode. To configure routing, use the ip route command.Source NAT
A CacheGuard appliance can perform Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) on all outgoing traffic through its external interface, replacing the source IP with its own external IP address. This mode is called snat and can be activated using the mode snat on command.Transparent Web
A CacheGuard appliance can be transparently deployed in a network to intercept Web traffic for management (caching, filtering, etc.). In transparent mode, there is no need to configure Web browsers to use the CacheGuard appliance as a Web proxy. The simplest way to implement a CacheGuard appliance transparently is to use it as the default gateway to the Internet. This mode is called tweb (transparent) and can be activated using the mode tweb on (or mode transparent on) command. The transparent (or tweb) command can then be used to selectively intercept Web traffic.As HTTP is increasingly being replaced by HTTPS, the capabilities of transparent mode are significantly reduced. Fortunately, a CacheGuard appliance can also intercept HTTPS traffic. The transparent interception of HTTPS traffic is referred to as sslmediate mode and is described in the Function Modes section below. This mode is considered a function mode rather than a network mode because it involves managing SSL CA certificates in addition to network configuration.
Transparent Web SNAT
In transparent mode (tweb), intercepted Web traffic can either preserve real source IP addresses or be Source NATed with the CacheGuard appliance’s external IP address. The tnat (transparent NAT) mode activates (on) source IP address translation for transparently intercepted Web traffic. The tnat mode is activated by default. To deactivate it, use the mode tnat off command. Note that when tnat is deactivated, routed Web traffic must not be asymmetric with respect to the CacheGuard appliance (i.e. all incoming and outgoing Web traffic exchanged with clients should pass through the same network interface).Tagged VLANs
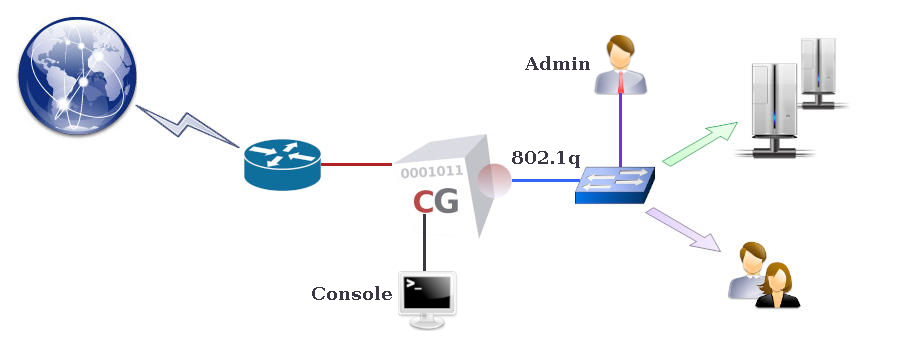
A CacheGuard appliance supports IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (Virtual LAN) tagging on its internal network interface to secure and isolate predefined functional traffic (admin, web, rweb, etc.). To activate VLAN mode, use the mode vlan on command. Once VLAN mode is activated, use the vlan and ip commands to define VLANs and assign IP addresses.If both web and rweb modes are activated on the same appliance, and SSL offloading is configured (where HTTPS traffic between the CacheGuard appliance and real Web servers is unencrypted), it is recommended to use a distinct VLAN for rweb traffic. Refer to the rweb command to learn how to configure the rweb mode for SSL offloading.
Function Modes
This section provides a brief description of all function modes. Available function modes operate at the application layer and are as follows:- Anonymous Browsing
- Antivirus
- Web Authentication
- Stateful Firewall
- Forwarding Web Proxy
- HTTP Compression
- OCSP Responder
- Reverse Web Proxy
- SSL Mediation
- Traffic Logging
- URL Guarding
- IPsec VPN
- Web Application Firewall
- Web Caching